When it comes to treatment for high cholesterol, interventions such as diet and exercise, new therapies such as PCSK9-inhibitors and older and traditional statins can help lower the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in people with high cholesterol blood levels. However, without the proper diagnostic tests, patients may not be matched with the best treatment plan for their individual risk. Improving CVD risk assessment can lead to improved CVD treatment and halting or slowing progression by more appropriately matching the type of therapy to the patient's risk.

NEW STUDY PUBLISHED
A new study from researchers from Quest Diagnostics and Skåne University Hospital, Malmö, Sweden provides insight into the value of a specialized type of testing that could help physicians identify the type of cholesterol-lowering therapy for their at-risk patients. The study, titled “
LDL subfractions are associated with incident cardiovascular disease in the Malmö Prevention Project Study,” was published in the August 2017 issue of the journal
Atherosclerosis. It investigated whether lipoprotein subfraction levels could aid in treatment decisions by assessing the association between lipoprotein subfractions and CVD, after adjustment for traditional risk factors including standard lipids ( LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, and triglycerides). Subfractionation is the process of separating lipoprotein particles by their size and measuring particle number of each size fraction.Using a case-cohort design, participants without CVD were randomly drawn from the Malmö Prevention Project (MPP), a population-based prospective study of 18,240 participants, and supplemented with additional participants with CVD events during follow-up (5,764 participants and 1,784 CVD events).The study found that measuring subfractions after adjusting for traditional risk factors could improve CVD risk assessment, thus enabling the healthcare professional to identify who should be on high intensity statin therapy prior to considering expensive PCSK9 inhibitor therapy for some patients. Lipoprotein subfraction test result can also help identify high risk patients among those with low to moderate risk (those with LDL-C <130 mg/dL and without diabetes). The researchers also noted that treatment selection should also include a discussion between the patient and treating physician about risk of CVD progression and willingness to modify behavior and take medication.
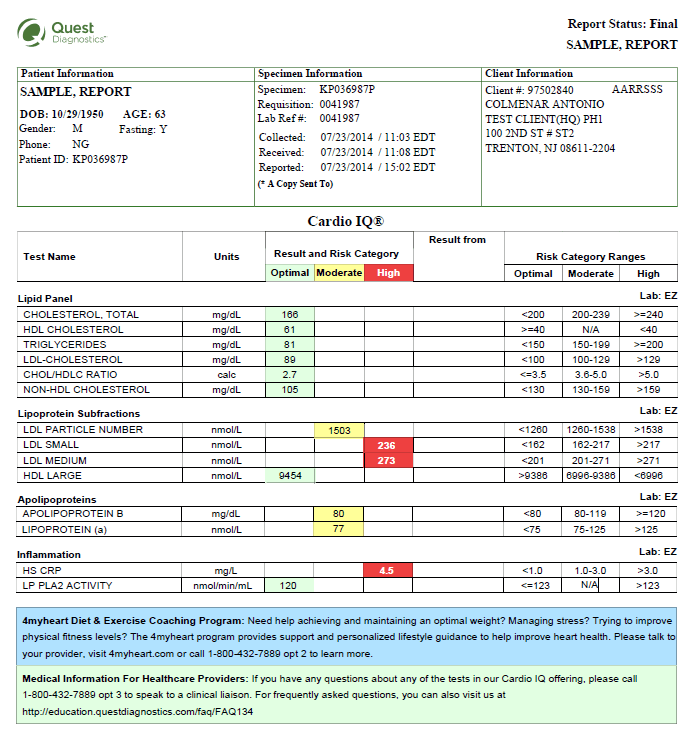
CARDIO IQ® OFFERS COMPLETE PICTURE
Quest Diagnostics is a leader in cardiovascular testing. Our
Cardio IQ® testing, which include LDL subfractionation, can offer a more complete picture of a patients’ cardiovascular health when available with conventional cholesterol screening. The test separates, counts and measures the particles that make up LDL-C and HDL-C. Low-density lipoprotein particles (LDL-P) are a strong predictor of cardiovascular risk beyond a basic lipid panel. A high number of small and medium LDL particles indicate an increased risk for heart disease. A low number of large HDL particles indicate increased risk for heart disease.As evidenced by the
Atherosclerosis study, knowing a patient’s particle number in addition to the traditional lipid panel may help a doctor better manage his or her patient’s treatment regimen to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Your Privacy Choices






